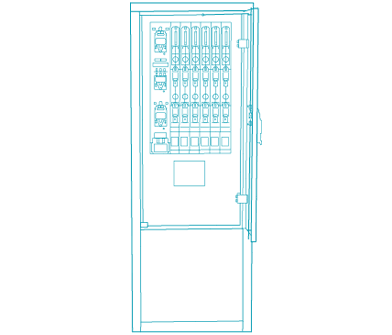
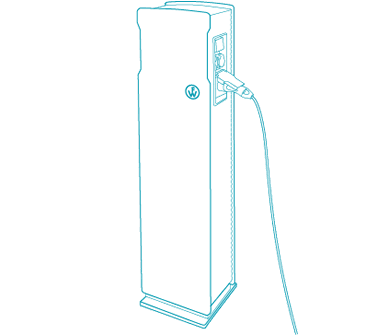
Charging cables
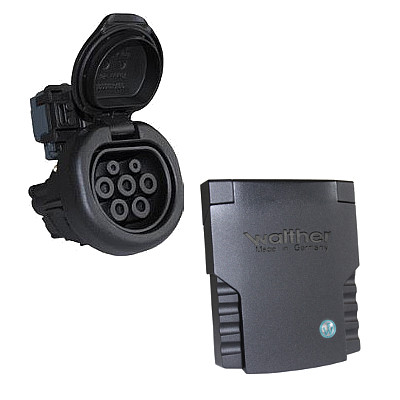
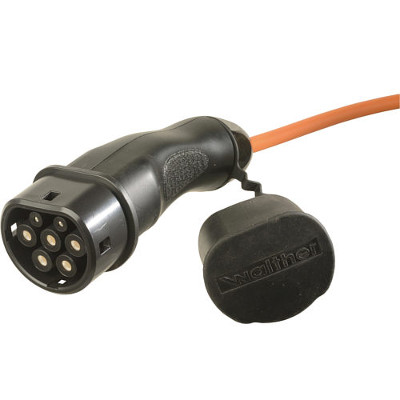
The charging cable establishes the electrical connection between the charging station and the electric vehicle. It includes the matching charger plug to the charger socket (Type 2) for pluggable charging cables and, on the vehicle side, a charger coupling (Type 1 or Type 2) to match the charger plug. IEC 62196 and IEC 61851 standards allow charging currents of 13, 16/20, 32 or 63 A. Depending on the vehicle, weight and handling appropriate charging cables are available. The type of charger coupling is selected according to the vehicle, as is the maximum charging current and cable length.